
In theory, if the matrix layer becomes thin enough, significant meniscus formation and subsequent cell pooling would be overcome. The smallest volume of matrix used in this assay to date is 15 μl/cm 2 (30 μl per well of a 24-well plate) which is more cost effective than the recommended volume of 50 μl/cm 2 (100 μl per well of a 24-well plate) but created a meniscus that promoted cell pooling. The use of a basement matrix in the study of anchorage-dependent differentiation is common place in many research laboratories, with the endothelial cell tube formation assay being the most widely used in vitro assay for the study of angiogenesis. This simple assay generates comparable data to those derived from large volume matrix assays, and has a far greater utility in terms of imaging and transcriptional analysis accompanied by a 25–30 fold reduction in relative cost. Here, we show that spreading low volumes of Geltrex™ basement membrane thinly onto glass or tissue culture plastic enables the use of high-resolution imaging and direct RNA extraction from endothelial cells that are actively engaged in the tube-forming process. In an attempt to solve these issues we sought to develop a thin layer angiogenesis assay (TLA) that would retain the ability to act as an anchoring and differentiating platform, but could also be used for high definition single cell imaging. dispase digestion) in order to extract mRNA for subsequent gene expression analysis. As well as increasing the general cost associated with performing these assays this volume of matrix also precludes the use of experimental techniques such as high-resolution/single cell microscopy and requires further cell manipulation (e.g. To study cell differentiation, a relatively large volume of matrix is usually indicated with recommendations and common usage of matrix in the order of 50-200 μl/cm 2, depending upon the assay to be employed. The most common assay employed using basement matrix is the EC tube formation assay, thought to represent the differentiation stage of angiogenesis and often being applied as a first-pass screening assay of compounds with potential pro- or anti-angiogenic properties (reviewed in Staton et al., 2009 ). These cell differentiation assays include the morphogenesis of endothelial cells (EC) into tube-like structures (tube-formation assay) for the study of in vitro angiogenesis, and the differentiation of neural cells in neurite outgrowth assays. Secreted extracellular matrix proteins, purified from the Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm (EHS) tumour, such as Matrigel™ and Geltrex™, are widely used in a variety of cell culture applications -, including the support of primary cell propagation, and anchorage-dependent cell differentiation.
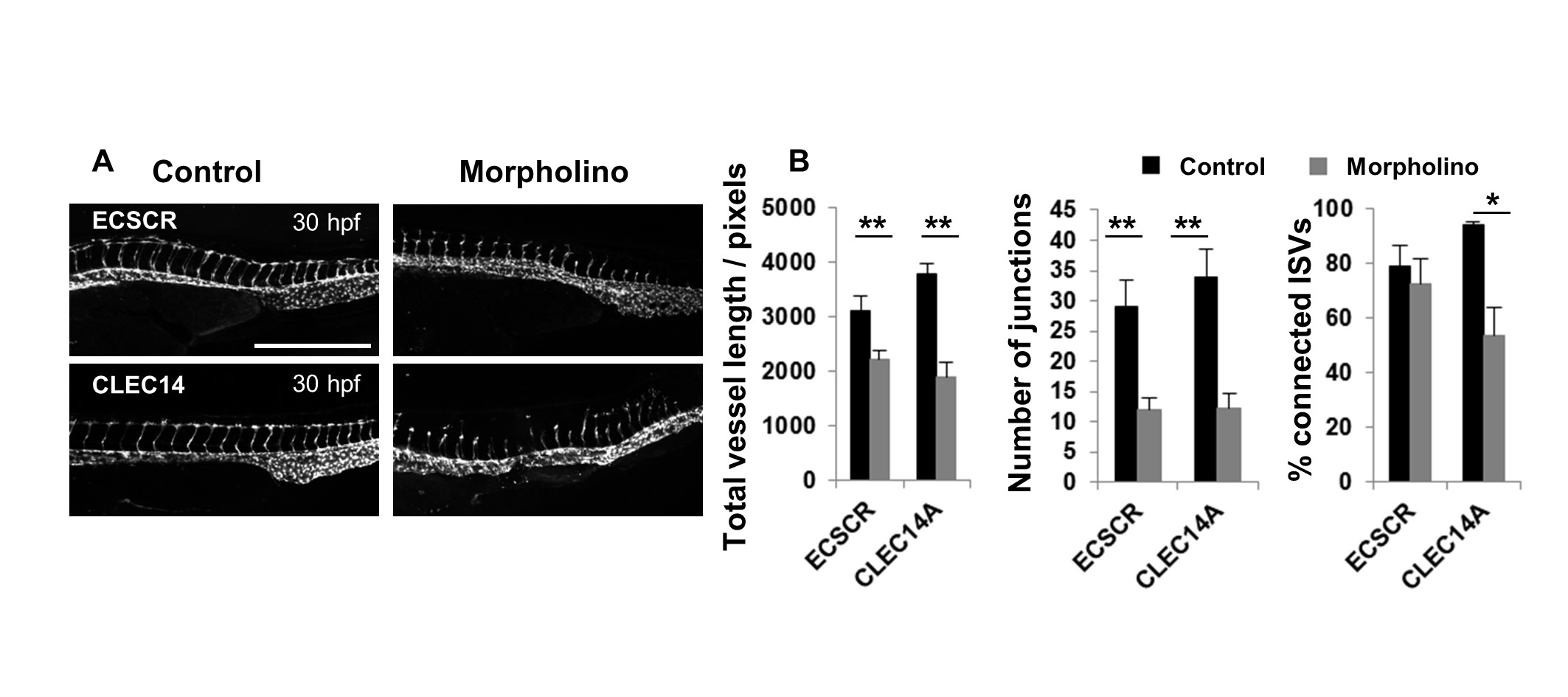
We present here a new thin-layer assay (TLA) for measuring the anchorage-dependent differentiation of endothelial cells into tube-like structures which retains all the characteristics of the traditional approach but with the added benefit of a greatly lowered cost and better compatibility with other techniques, including RT-qPCR and high-resolution microscopy. Using a standard commercial total RNA extraction kit (Qiagen) we also show direct RNA extraction and RT-qPCR from differentiated endothelial cells without the need to initially detach cells from their supporting matrix. Using MitoTracker dye we now demonstrate, for the first time, live mitochondrial dynamics and visualise the 3-dimensional network of mitochondria present in differentiated endothelial cells.

Since working distances are reduced, high-resolution single cell microscopy, including DIC and confocal imaging, can be used readily. Geltrex™ basement matrix at 5 μl/cm 2 in 24-well (10 μl) or 96-well (2 μl) plates supports endothelial cell differentiation into tube-like structures in a comparable manner to the standard larger volumes of matrix. Here we describe the development and validation of a thin-layer angiogenesis (TLA) assay for assessing the angiogenic potential of endothelial cells that overcomes these limitations. The volumes of matrix recommended for these assays (approximately 150 μl/cm 2) are costly, limit working distances for microscopy, and require cell detachment for subsequent molecular analysis. Basement matrices such as Matrigel™ and Geltrex™ are used in a variety of cell culture assays of anchorage-dependent differentiation including endothelial cell tube formation assays.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
